Code
The code is available on github here.
Skills
- Deep Learning
- Neural Networks
- Python
- PyTorch
- Text Processing
- Natural Language Processing
About
This project was part of the QMBU450 Advanced Data Science with Python course at Koç University.
I used the Amazon Fine Food Reviews dataset to train an LSTM Model to predict the sentiment of the food reviews as a rating that takes an integer value in the range [1,5] (which means have 5 classes).
Motivation
As a course requirement, we had the freedom to choose any machine learning problem to work on. I chose this particular problem because I was interested in learning about NLP as I had no prior experience. Spending the semester on learning different concepts and techniques, and then putting them into practice was so much fun. My interest in NLP grew significantly after this experience.
What is LSTM ?
A variation Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) which is capable of learning long-term dependencies of sequenced data (Hence the Abbreviation Long Short Term Memory).
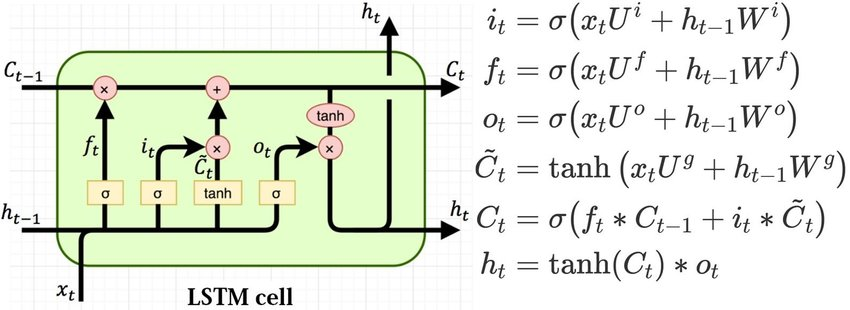
If you would like to learn more about LSTMs here is a wonderful link.
Packages Used
I used the following python packages:
cupy: Used to make numpy operations on gpu.nltk: Has very useful builtin functions for text processing as well as lists of stop words.spacy: A high level NLP package with advanced functionalities such is lemmatization, and pre-trained word embeddings.gensim: Has an implementation for Word2Vec algorithm, which allows for generating a custom set of word vectors for the dataset.torch: A Deep Learning Framework which supports the LSTM structure.
Preprocessing
First, the textual data was pre-processed with some standard operations such as:
- Make everything lowercase
- Expand Contractions
- Remove HTML tags
- Remove Multiple Spaces
- Remove Special Characters
- Remove Punctuation
- Tokenize
After the initial cleaning, we need to replace each textual word with its word embedding representation. This is a vector that represents the semantics of a word. Two similar words or words used in similar contexts have similar vectors (similarity can be measured using cosine similarity). There are several ways to do so. We could either use already pre-trained word embeddings, or train our own customized set of word vectors.
Custom Trained Word Embeddings
We can use the famous Word2Vec algorithm to generate word vectors specific to our dataset. This works well if the size of the dataset is large enough. Otherwise, the vectors will overfit on the training data and it will perform poorly when the context is changed. Not to mention that training it takes too much time.
Pre-Trained Word embeddings
There are several famous pre-trained word embeddings such as GloVe, which are trained on large textual dataset in order to capture the best semantics and largest range of words. These vectors come in different dimensions. The greater the dimensions the better it represents the meaning, but at the cost of longer training time.
I have used GloVe vectors in the project in order to save time training and to avoid overfitting on the training data.
Model
The nice thing about python is that it has many packages that support different levels of implementations for many useful tools in machine learning.
For this project I used PyTorch framework, which supports several advanced neural network structures with the ease of deploying and stacking different components with few lines of code.