publications
All of my publications in chronological order.
2025
- IJCV
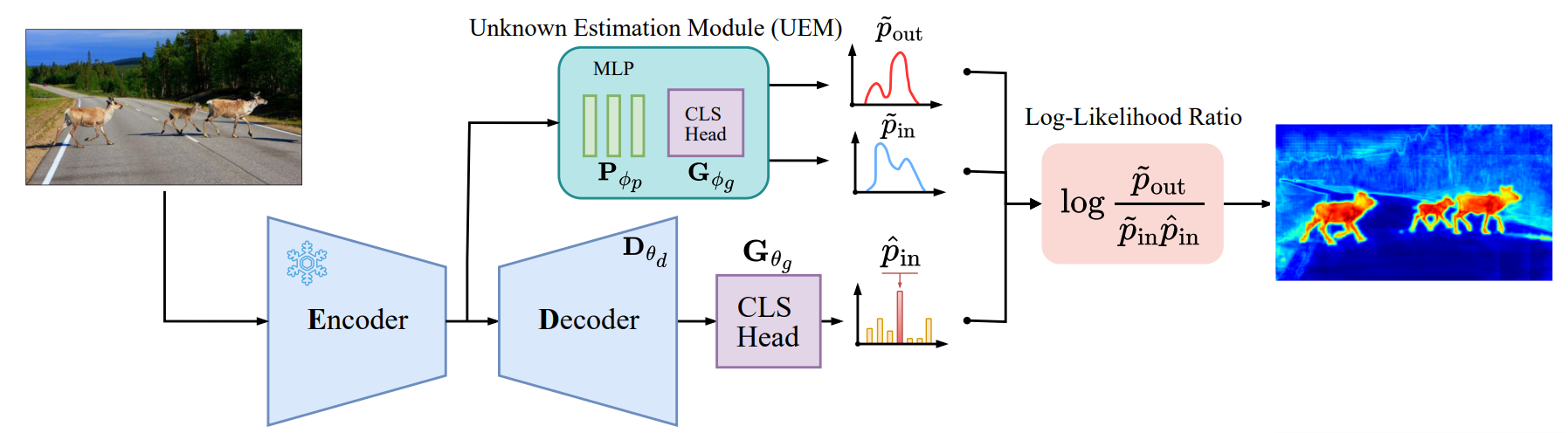 A Likelihood Ratio-Based Approach to Segmenting Unknown ObjectsNazir Nayal, Youssef Shoeb, and Fatma GüneyInternational Journal of Computer Vision, 2025
A Likelihood Ratio-Based Approach to Segmenting Unknown ObjectsNazir Nayal, Youssef Shoeb, and Fatma GüneyInternational Journal of Computer Vision, 2025Addressing the Out-of-Distribution (OoD) segmentation task is a prerequisite for perception systems operating in an open-world environment. Large foundational models are frequently used in downstream tasks, however, their potential for OoD remains mostly unexplored. We seek to leverage a large foundational model to achieve robust representation. Outlier supervision is a widely used strategy for improving OoD detection of the existing segmentation networks. However, current approaches for outlier supervision involve retraining parts of the original network, which is typically disruptive to the model’s learned feature representation. Furthermore, retraining becomes infeasible in the case of large foundational models. Our goal is to retrain for outlier segmentation without compromising the strong representation space of the foundational model. To this end, we propose an adaptive, lightweight unknown estimation module (UEM) for outlier supervision that significantly enhances the OoD segmentation performance without affecting the learned feature representation of the original network. UEM learns a distribution for outliers and a generic distribution for known classes. Using the learned distributions, we propose a likelihood-ratio-based outlier scoring function that fuses the confidence of UEM with that of the pixel-wise segmentation inlier network to detect unknown objects. We also propose an objective to optimize this score directly. Our approach achieves a new state-of-the-art across multiple datasets, outperforming the previous best method by 5.74% average precision points while having a lower false-positive rate. Importantly, strong inlier performance remains unaffected.
@article{nayal2024likelihood, title = {A Likelihood Ratio-Based Approach to Segmenting Unknown Objects}, author = {Nayal, Nazir and Shoeb, Youssef and G{\"u}ney, Fatma}, journal = {International Journal of Computer Vision}, year = {2025}, } - VISAPP 2025
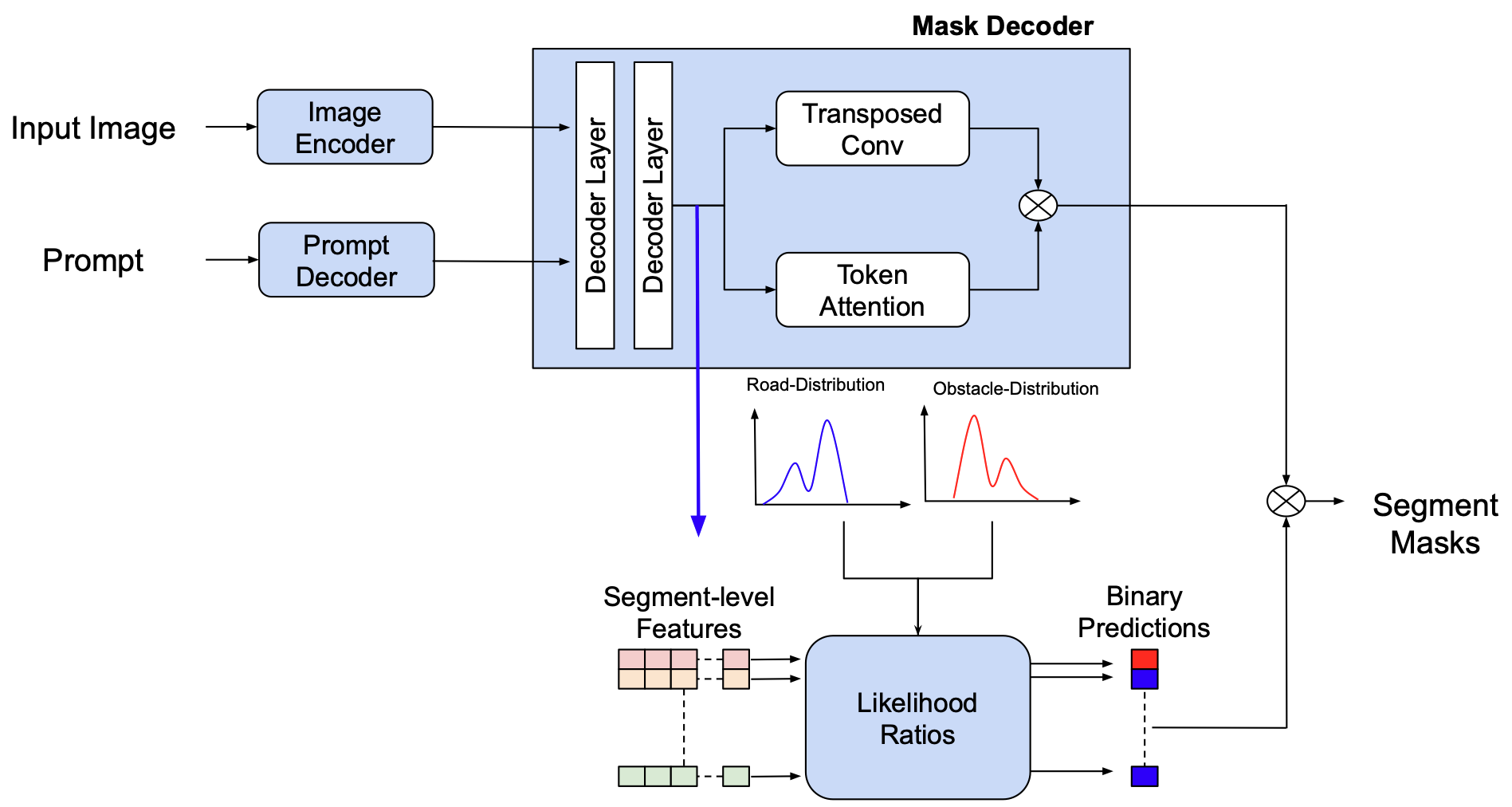 Segment-Level Road Obstacle Detection Using Visual Foundation Model Priors and Likelihood RatiosYoussef Shoeb, Nazir Nayal, Azarm Nowzard, Fatma Güney, and Hanno GottschalkInternational Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications (VISAPP), 2025
Segment-Level Road Obstacle Detection Using Visual Foundation Model Priors and Likelihood RatiosYoussef Shoeb, Nazir Nayal, Azarm Nowzard, Fatma Güney, and Hanno GottschalkInternational Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications (VISAPP), 2025Detecting road obstacles is essential for autonomous vehicles to navigate dynamic and complex traffic environments safely. Current road obstacle detection methods typically assign a score to each pixel and apply a threshold to generate final predictions. However, selecting an appropriate threshold is challenging, and the per-pixel classification approach often leads to fragmented predictions with numerous false positives. In this work, we propose a novel method that leverages segment-level features from visual foundation models and likelihood ratios to predict road obstacles directly. By focusing on segments rather than individual pixels, our approach enhances detection accuracy, reduces false positives, and offers increased robustness to scene variability. We benchmark our approach against existing methods on the RoadObstacle and LostAndFound datasets, achieving state-of-the-art performance without needing a predefined threshold.
@article{shoeb2024segmentlevelroadobstacledetection, title = {Segment-Level Road Obstacle Detection Using Visual Foundation Model Priors and Likelihood Ratios}, author = {Shoeb, Youssef and Nayal, Nazir and Nowzard, Azarm and Güney, Fatma and Gottschalk, Hanno}, year = {2025}, journal = {International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications (VISAPP)}, url = {https://arxiv.org/abs/2412.05707}, }
2023
- RbA: Segmenting Unknown Regions Rejected by AllNazir Nayal, Mısra Yavuz, João F. Henriques, and Fatma GüneyIn Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), 2023
Standard semantic segmentation models owe their success to curated datasets with a fixed set of semantic categories, without contemplating the possibility of identifying unknown objects from novel categories. Existing methods in outlier detection suffer from a lack of smoothness and objectness in their predictions, due to limitations of the per-pixel classification paradigm. Furthermore, additional training for detecting outliers harms the performance of known classes. In this paper, we explore another paradigm with region-level classification to better segment unknown objects. We show that the object queries in mask classification tend to behave like one vs. all classifiers. Based on this finding, we propose a novel outlier scoring function called RbA by defining the event of being an outlier as being rejected by all known classes. Our extensive experiments show that mask classification improves the performance of the existing outlier detection methods, and the best results are achieved with the proposed RbA. We also propose an objective to optimize RbA using minimal outlier supervision. Further fine-tuning with outliers improves the unknown performance, and unlike previous methods, it does not degrade the inlier performance.
@inproceedings{nayal2023ICCV, author = {Nayal, Nazir and Yavuz, Mısra and Henriques, João F. and Güney, Fatma}, title = {RbA: Segmenting Unknown Regions Rejected by All}, booktitle = {Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV)}, year = {2023}, }
2020
- ICBC 2020
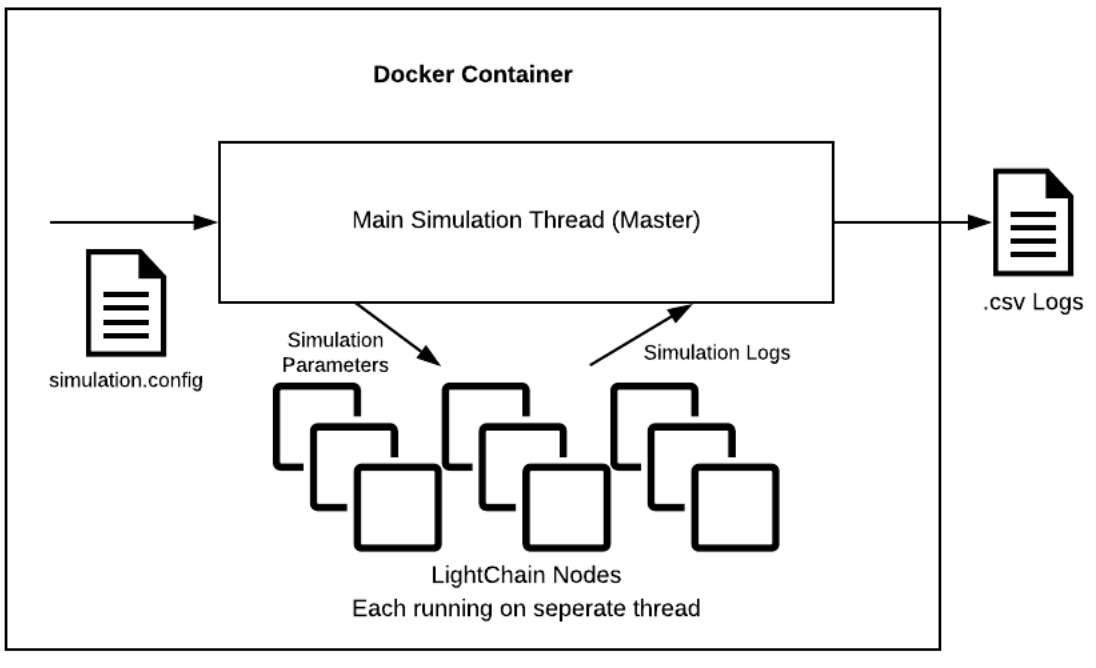 A containerized proof-of-concept implementation of LightChain systemYahya Hassanzadeh-Nazarabadi, Nazir Nayal, Shadi Sameh Hamdan, Öznur Özkasap, and Alptekin KüpçüIn 2020 IEEE International Conference on Blockchain and Cryptocurrency (ICBC), 2020
A containerized proof-of-concept implementation of LightChain systemYahya Hassanzadeh-Nazarabadi, Nazir Nayal, Shadi Sameh Hamdan, Öznur Özkasap, and Alptekin KüpçüIn 2020 IEEE International Conference on Blockchain and Cryptocurrency (ICBC), 2020@inproceedings{9169463, author = {Hassanzadeh-Nazarabadi, Yahya and Nayal, Nazir and Hamdan, Shadi Sameh and Özkasap, Öznur and Küpçü, Alptekin}, booktitle = {2020 IEEE International Conference on Blockchain and Cryptocurrency (ICBC)}, title = {A containerized proof-of-concept implementation of LightChain system}, year = {2020}, volume = {}, number = {}, pages = {1-2}, keywords = {Peer-to-peer computing;Middleware;Complexity theory;Message systems;Java;Blockchain;Simulation;Docker;Distributed Hash Tables}, doi = {10.1109/ICBC48266.2020.9169463}, } - SRDS 2020
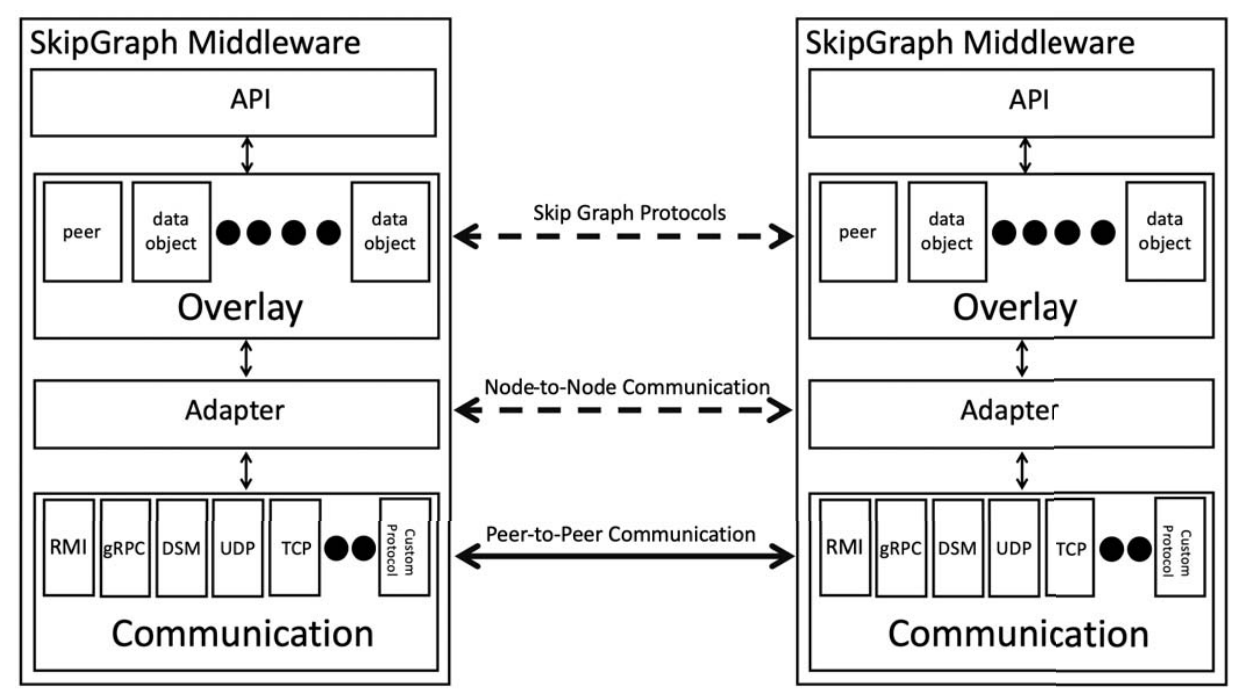 Demo: Skip Graph Middleware ImplementationYahya Hassanzadeh-Nazarabadi, Nazir Nayal, Shadi Sameh Hamdan, Ali Utkan Şahin, Öznur Özkasap, and 1 more authorIn 2020 International Symposium on Reliable Distributed Systems (SRDS), 2020
Demo: Skip Graph Middleware ImplementationYahya Hassanzadeh-Nazarabadi, Nazir Nayal, Shadi Sameh Hamdan, Ali Utkan Şahin, Öznur Özkasap, and 1 more authorIn 2020 International Symposium on Reliable Distributed Systems (SRDS), 2020@inproceedings{9252072, author = {Hassanzadeh-Nazarabadi, Yahya and Nayal, Nazir and Hamdan, Shadi Sameh and Şahin, Ali Utkan and Özkasap, Öznur and Küpçü, Alptekin}, booktitle = {2020 International Symposium on Reliable Distributed Systems (SRDS)}, title = {Demo: Skip Graph Middleware Implementation}, year = {2020}, volume = {}, number = {}, pages = {335-337}, keywords = {Software architecture;Memory;Routing;Peer-to-peer computing;Reliability;Middleware;Open source software;Skip Graph;Overlay;P2P;Distributed Hash Table;Java;Implementation}, doi = {10.1109/SRDS51746.2020.00042}, }
